Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Loop Finding and Analysis¶
This example demonstrates how to find and analyze loops in polymer networks using pylimer-tools.
Number of loops found (max length 2*(46+1)): 2
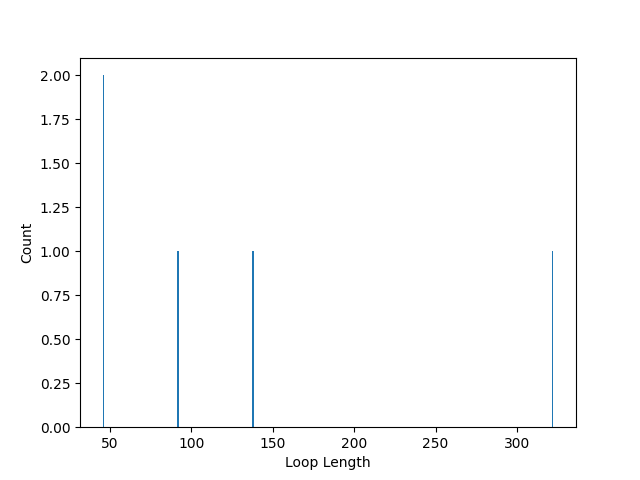
Loop length counts: {322: 1, 92: 1, 46: 2, 138: 1}
Shortest loop involving atom 1: []
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pylimer_tools.io.read_lammps_output_file import read_data_file
from pylimer_tools_cpp import Universe
# Replace with your crosslinker type
crosslinker_type = 2
# Load your network (replace 'network.gml' with your file)
universe = read_data_file(
os.path.join(
os.getcwd(),
"../..",
"tests/pylimer_tools/fixtures/structure/network_100_a_46.structure.out",
)
)
assert isinstance(universe, Universe)
# 1. Find loops in the network
loops = universe.find_loops(
crosslinker_type, skip_self_loops=True, max_length=2 * (46 + 1)
) # restrict for large networks
print(f"Number of loops found (max length 2*(46+1)): {len(loops)}")
# 2. Count loop lengths
loop_length_counts = universe.count_loop_lengths(max_length=7 * (46 + 1))
print(f"Loop length counts: {loop_length_counts}")
# plot the loop length counts
plt.bar(list(loop_length_counts.keys()), list(loop_length_counts.values()))
plt.xlabel("Loop Length")
plt.ylabel("Count")
plt.show()
# 3. Find shortest loop for a specific atom (e.g., atom 0)
shortest_loop = universe.find_minimal_order_loop_from(
loop_start=1, loop_step1=1)
print(f"Shortest loop involving atom 1: {shortest_loop}")
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.106 seconds)