Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Deformation Experiment¶
This example shows how to use the MEHPForceBalance2 class in a deformation experiment.
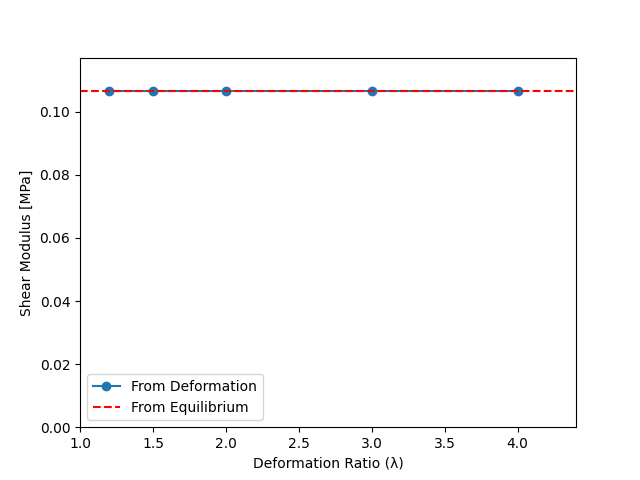
It also shows, that deformation is an equivalent method to the \(\Gamma\) factor to obtain the modulus.
import copy
import math
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from pylimer_tools.io.bead_spring_parameter_provider import (
ParameterType,
Parameters,
get_parameters_for_polymer,
)
from pylimer_tools.io.read_lammps_output_file import read_data_file
from pylimer_tools_cpp import Box, MEHPForceBalance2, Universe
# Get parameters for conversion factors
params = get_parameters_for_polymer(
"PDMS", parameter_type=ParameterType.GAUSSIAN)
assert isinstance(params, Parameters)
# Load your network (replace with your file)
universe = read_data_file(
os.path.join(
os.getcwd(),
"../..",
"tests/pylimer_tools/fixtures/structure/network_100_a_46.structure.out",
)
)
assert isinstance(universe, Universe)
# 2. MEHPForceBalance: Hookean springs, allows slip-links
mehp_fb = MEHPForceBalance2(
universe,
nr_of_entanglements_to_sample=int(
params.get_entanglement_density() * universe.get_volume()
),
upper_sampling_cutoff=params.get_sampling_cutoff(),
entanglements_as_springs=False,
)
mehp_fb.run_force_relaxation()
print(
"Final residual (should be close to 0):", mehp_fb.get_displacement_residual_norm()
)
# apply conversion factors, measure resulting shear modulus
r02_slope = params.get("R02")
r02_slope_magnitude = r02_slope.to(params.get("distance_units") ** 2).magnitude
kbt = params.get("T") * params.get("kb")
gamma_conversion_factor = (
(kbt / ((params.get("distance_units")) ** 3)).to("MPa").magnitude
)
shear_modulus = (
gamma_conversion_factor
* np.sum(mehp_fb.get_gamma_factors(r02_slope_magnitude))
/ universe.get_volume()
)
print("Shear Modulus from Equilibrium [MPa]: ", shear_modulus)
moduli_deformed = []
lmbdas = [1.2, 1.5, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0]
box_0 = universe.get_box()
l0 = box_0.get_lx()
assert math.isclose(l0, box_0.get_ly())
assert math.isclose(l0, box_0.get_lz())
mehp_fb_original = copy.copy(mehp_fb)
for lmbda in lmbdas:
this_moduli_deformed = []
for dir in range(3):
mehp_fb = copy.copy(mehp_fb_original)
# deform the box in one direction
new_box = Box(
l0 * lmbda if dir == 0 else l0 * 1 / (lmbda**0.5),
l0 * lmbda if dir == 1 else l0 * 1 / (lmbda**0.5),
l0 * lmbda if dir == 2 else l0 * 1 / (lmbda**0.5),
)
assert math.isclose(box_0.get_volume(), new_box.get_volume())
mehp_fb.deform_to(new_box)
mehp_fb.run_force_relaxation()
stress_tensor = mehp_fb.get_stress_tensor()
# remove the pressure contribution using the nominal stress
sigma_n = (
stress_tensor[dir][dir]
- (
stress_tensor[(dir + 1) % 3][(dir + 1) % 3]
+ stress_tensor[(dir + 2) % 3][(dir + 2) % 3]
)
/ 2
)
# compute the shear modulus from the nominal stress
this_moduli_deformed.append(sigma_n / (lmbda**2 - 1 / lmbda))
assert len(this_moduli_deformed) == 3
moduli_deformed.append(
np.mean(this_moduli_deformed) * params.get_fb_stress_conversion()
)
# plot deformation results
plt.figure()
plt.plot(lmbdas, moduli_deformed, marker="o", label="From Deformation")
plt.axhline(
y=shear_modulus,
color="r",
linestyle="--",
label="From Equilibrium")
plt.xlabel("Deformation Ratio (λ)")
plt.ylabel("Shear Modulus [MPa]")
plt.ylim(0, max(moduli_deformed) * 1.1)
plt.xlim(1, max(lmbdas) * 1.1)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
Final residual (should be close to 0): 3.060142298004421e-13
Shear Modulus from Equilibrium [MPa]: 0.1014205420402294
Rather than using the nominal stress, you can also use the stress tensor directly to compute the shear modulus. Therewith, you could try to investigate e.g. the Mooney-Rivlin behaviour.
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.012 seconds)